- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Application of an Array of Metal-Oxide Semiconductor Gas Sensors in an Assistant Personal Robot for Early Gas Leak Detection
Read this article at
Abstract
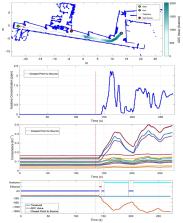
This paper proposes the application of a low-cost gas sensor array in an assistant personal robot (APR) in order to extend the capabilities of the mobile robot as an early gas leak detector for safety purposes. The gas sensor array is composed of 16 low-cost metal-oxide (MOX) gas sensors, which are continuously in operation. The mobile robot was modified to keep the gas sensor array always switched on, even in the case of battery recharge. The gas sensor array provides 16 individual gas measurements and one output that is a cumulative summary of all measurements, used as an overall indicator of a gas concentration change. The results of preliminary experiments were used to train a partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) classifier with air, ethanol, and acetone as output classes. Then, the mobile robot gas leak detection capabilities were experimentally evaluated in a public facility, by forcing the evaporation of (1) ethanol, (2) acetone, and (3) ethanol and acetone at different locations. The positive results obtained in different operation conditions over the course of one month confirmed the early detection capabilities of the proposed mobile system. For example, the APR was able to detect a gas leak produced inside a closed room from the external corridor due to small leakages under the door induced by the forced ventilation system of the building.
Related collections
Most cited references48

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Metal Oxide Gas Sensors: Sensitivity and Influencing Factors

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Metal Oxide Semi-Conductor Gas Sensors in Environmental Monitoring
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found