- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Combined PARP Inhibition and Immune Checkpoint Therapy in Solid Tumors
Read this article at
Abstract
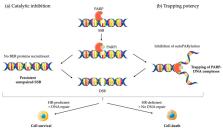
Genomic instability is a hallmark of cancer related to DNA damage response (DDR) deficiencies, offering vulnerabilities for targeted treatment. Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) inhibitors (PARPi) interfere with the efficient repair of DNA damage, particularly in tumors with existing defects in DNA repair, and induce synthetic lethality. PARPi are active across a range of tumor types harboring BRCA mutations and also BRCA-negative cancers, such as ovarian, breast or prostate cancers with homologous recombination deficiencies (HRD). Depending on immune contexture, immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs), such as anti-PD1/PD-L1 and anti-CTLA-4, elicit potent antitumor effects and have been approved in various cancers types. Although major breakthroughs have been performed with either PARPi or ICIs alone in multiple cancers, primary or acquired resistance often leads to tumor escape. PARPi-mediated unrepaired DNA damages modulate the tumor immune microenvironment by a range of molecular and cellular mechanisms, such as increasing genomic instability, immune pathway activation, and PD-L1 expression on cancer cells, which might promote responsiveness to ICIs. In this context, PARPi and ICIs represent a rational combination. In this review, we summarize the basic and translational biology supporting the combined strategy. We also detail preclinical results and early data of ongoing clinical trials indicating the synergistic effect of PARPi and ICIs. Moreover, we discuss the limitations and the future direction of the combination.
Related collections
Most cited references64
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The diverse functions of the PD1 inhibitory pathway

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Mechanisms of resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found