- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Bio-psycho-social factors’ associations with brain age: a large-scale UK Biobank diffusion study of 35,749 participants
Read this article at
Abstract
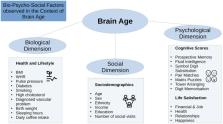
Brain age refers to age predicted by brain features. Brain age has previously been associated with various health and disease outcomes and suggested as a potential biomarker of general health. Few previous studies have systematically assessed brain age variability derived from single and multi-shell diffusion magnetic resonance imaging data. Here, we present multivariate models of brain age derived from various diffusion approaches and how they relate to bio-psycho-social variables within the domains of sociodemographic, cognitive, life-satisfaction, as well as health and lifestyle factors in midlife to old age ( N = 35,749, 44.6–82.8 years of age). Bio-psycho-social factors could uniquely explain a small proportion of the brain age variance, in a similar pattern across diffusion approaches: cognitive scores, life satisfaction, health and lifestyle factors adding to the variance explained, but not socio-demographics. Consistent brain age associations across models were found for waist-to-hip ratio, diabetes, hypertension, smoking, matrix puzzles solving, and job and health satisfaction and perception. Furthermore, we found large variability in sex and ethnicity group differences in brain age. Our results show that brain age cannot be sufficiently explained by bio-psycho-social variables alone. However, the observed associations suggest to adjust for sex, ethnicity, cognitive factors, as well as health and lifestyle factors, and to observe bio-psycho-social factor interactions’ influence on brain age in future studies.
Related collections
Most cited references117

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
UK Biobank: An Open Access Resource for Identifying the Causes of a Wide Range of Complex Diseases of Middle and Old Age
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found