- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Multiple Facets of Modeling Electronic Absorption Spectra of Systems in Solution
Read this article at
Abstract

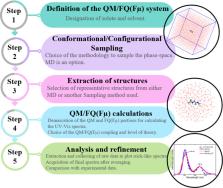
In this Perspective, we outline the essential physicochemical aspects that need to be considered when building a reliable approach to describe absorption properties of solvated systems. In particular, we focus on how to properly model the complexity of the solvation phenomenon, arising from dynamical aspects and specific, strong solute–solvent interactions. To this end, conformational and configurational sampling techniques, such as Molecular Dynamics, have to be coupled to accurate fully atomistic Quantum Mechanical/Molecular Mechanics (QM/MM) methodologies. By exploiting different illustrative applications, we show that an effective reproduction of experimental spectral signals can be achieved by delicately balancing exhaustive sampling, hydrogen bonding, mutual polarization, and nonelectrostatic effects.
Related collections
Most cited references117
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Quantum mechanical continuum solvation models.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found