- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Inflammation and Obesity: The Pharmacological Role of Flavonoids in the Zebrafish Model
Read this article at
Abstract
A Mediterranean-style diet is highly encouraged thanks to its healthy food pattern, which includes valuable nutraceuticals such as polyphenols. Among these, flavonoids are associated with relevant biological properties through which they prevent or fight the onset of several human pathologies. Globally, the enhanced incidence of overweight and obese people has caused a dramatic increase in comorbidities, raising the need to provide better therapies. Therefore, the development of sophisticated animal models of metabolic dysregulation has allowed for a deepening of knowledge on this subject. Recent advances in using zebrafish (Danio rerio) as model for metabolic disease have yielded fundamental insights into the potential anti-obesity effects of flavonoids. Chronic low-grade inflammation and immune system activation seem to characterize the pathogenesis of obesity; thus, their reduction might improve the lipid profile of obese patients or prevent the development of associated metabolic illnesses. In this review, we highlight the beneficial role of flavonoids on obesity and related diseases linked to their anti-inflammatory properties. In light of the summarized studies, we suggest that anti-inflammatory therapies could have a relevant place in the prevention and treatment of obesity and metabolic disorders.
Related collections
Most cited references106
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
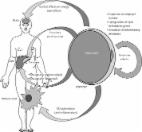
Inflammatory mechanisms linking obesity and metabolic disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found