- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Mechanically rigid supramolecular assemblies formed from an Fmoc-guanine conjugated peptide nucleic acid
Read this article at
Abstract
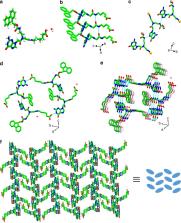
The variety and complexity of DNA-based structures make them attractive candidates for nanotechnology, yet insufficient stability and mechanical rigidity, compared to polyamide-based molecules, limit their application. Here, we combine the advantages of polyamide materials and the structural patterns inspired by nucleic-acids to generate a mechanically rigid fluorenylmethyloxycarbonyl (Fmoc)-guanine peptide nucleic acid (PNA) conjugate with diverse morphology and photoluminescent properties. The assembly possesses a unique atomic structure, with each guanine head of one molecule hydrogen bonded to the Fmoc carbonyl tail of another molecule, generating a non-planar cyclic quartet arrangement. This structure exhibits an average stiffness of 69.6 ± 6.8 N m −1 and Young’s modulus of 17.8 ± 2.5 GPa, higher than any previously reported nucleic acid derived structure. This data suggests that the unique cation-free “basket” formed by the Fmoc-G-PNA conjugate can serve as an attractive component for the design of new materials based on PNA self-assembly for nanotechnology applications.
Abstract
DNA is an attractive nanomaterial, yet limited compared to polyamides due to low stability and mechanical issues. Here, the authors combine polyamide and DNA characteristics to form mechanically rigid self-assembled peptide nucleic acid based materials with high stiffness and Young’s modulus.
Related collections
Most cited references72
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Generalized Gradient Approximation Made Simple
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
TOPAS and TOPAS-Academic: an optimization program integrating computer algebra and crystallographic objects written in C++
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found