- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comparison of the efficacy and safety of 2% lidocaine HCl with different epinephrine concentration for local anesthesia in participants undergoing surgical extraction of impacted mandibular third molars : A multicenter, randomized, double-blind, crossover, phase IV trial
Read this article at
Abstract
Background:
The most commonly impacted tooth is the third molar. An impacted third molar can ultimately cause acute pain, infection, tumors, cysts, caries, periodontal disease, and loss of adjacent teeth. Local anesthesia is employed for removing the third molar. This study aimed to evaluate the efficacy and safety of 2% lidocaine with 1:80,000 or 1:200,000 epinephrine for surgical extraction of bilateral impacted mandibular third molars.
Methods:
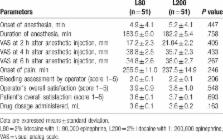
Sixty-five healthy participants underwent surgical extraction of bilateral impacted mandibular third molars in 2 separate visits while under local anesthesia with 2% lidocaine with different epinephrine concentration (1:80,000 or 1:200,000) in a double-blind, randomized, crossover trial. Visual analog scale pain scores obtained immediately after surgical extraction were primarily evaluated for the 2 groups receiving different epinephrine concentrations. Visual analog scale pain scores were obtained 2, 4, and 6 hours after administering an anesthetic. Onset and duration of analgesia, onset of pain, intraoperative bleeding, operator's and participant's overall satisfaction, drug dosage, and hemodynamic parameters were evaluated for the 2 groups.
Results:
There were no statistically significant differences between the 2 groups in any measurements except hemodynamic factors ( P >.05). Changes in systolic blood pressure and heart rate following anesthetic administration were significantly greater in the group receiving 1:80,000 epinephrine than in that receiving 1:200,000 epinephrine ( P ≤.01).
Conclusion:
The difference in epinephrine concentration between 1:80,000 and 1:200,000 in 2% lidocaine liquid does not affect the medical efficacy of the anesthetic. Furthermore, 2% lidocaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine has better safety with regard to hemodynamic parameters than 2% lidocaine with 1:80,000 epinephrine. Therefore, we suggest using 2% lidocaine with 1:200,000 epinephrine rather than 2% lidocaine with 1:80,000 epinephrine for surgical extraction of impacted mandibular third molars in hemodynamically unstable patients.
Related collections
Most cited references28
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Graphic representation of pain.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A comparison of the visual analogue scale and modified Borg scale for the measurement of dyspnoea during exercise.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found