- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
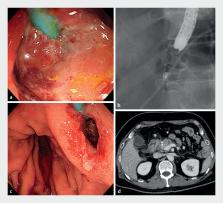
Severe bleeding associated with lumen-apposing metal stent placement for walled-off necrosis: bloody memory in WONderland
research-article
Shuichi Tange , Dr.,
Tomotaka Saito , Dr.,
Yousuke Nakai , MD,
Tsuyoshi Hamada , Dr.,
Yusuke Watanabe , Dr.,
Naminatsu Takahara , Dr.,
Mitsuhiro Fujishiro
25 June 2024
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
Related collections
Most cited references5
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
International multicenter comprehensive analysis of adverse events associated with lumen-apposing metal stent placement for pancreatic fluid collection drainage
Alessandro Fugazza, Amrita Sethi, Arvind Trindade … (2019)
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found