- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) and Cytokine Storms for More Effective Treatments from an Inflammatory Pathophysiology
Read this article at
Abstract
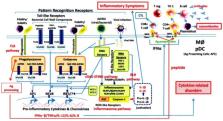
The Novel Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) has swept the world and caused a global pandemic. SARS-CoV-2 seems to have originated from bats as their reservoir hosts over time. Similar to SARS-CoV, this new virus also exerts its action on the human angiotensin-converting enzyme 2. This action causes infections in cells and establishes an infectious disease, COVID-19. Against this viral invasion, the human body starts to activate the innate immune system in producing and releasing proinflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-1β, IL-8, TNF-α, and other chemokines, such as G-CSF, IP10 and MCPl, which all develop and increase the inflammatory response. In cases of COVID-19, excessive inflammatory responses occur, and exaggerated proinflammatory cytokines and chemokines are detected in the serum, resulting in cytokine release syndrome or cytokine storm. This causes coagulation abnormalities, excessive oxidation developments, mitochondrial permeability transition, vital organ damage, immune system failure and eventually progresses to disseminated intravascular coagulation and multiple organ failure. Additionally, the excessive inflammatory responses also cause mitochondrial dysfunction due to progressive and persistent stress. This damages cells and mitochondria, leaving products containing mitochondrial DNA and cell debris involved in the excessive chronic inflammation as damage-associated molecular patterns. Thus, the respiratory infection progressively leads to disseminated intravascular coagulation from acute respiratory distress syndrome, including vascular endothelial cell damage and coagulation-fibrinolysis system disorders. This condition causes central nervous system disorders, renal failure, liver failure and, finally, multiple organ failure. Regarding treatment for COVID-19, the following are progressive and multiple steps for mitigating the excessive inflammatory response and subsequent cytokine storm in patients. First, administering of favipiravir to suppress SARS-CoV-2 and nafamostat to inhibit ACE2 function should be considered. Second, anti-rheumatic drugs (monoclonal antibodies), which act on the leading cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6) and/or cytokine receptors such as tocilizumab, should be administered as well. Finally, melatonin may also have supportive effects for cytokine release syndrome, resulting in mitochondrial function improvement. This paper will further explore these subjects with reports mostly from China and Europe.
Related collections
Most cited references62
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical features of patients infected with 2019 novel coronavirus in Wuhan, China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found