- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Spontaneous pregnancies among infertile couples during assisted reproduction lockdown for COVID‐19 pandemic
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The worldwide spread of the SARS‐CoV‐2 infection has profoundly affected all aspects of human life, with tangible consequences in several contexts, including reproduction. However, evidences on the inter‐relation between psychological distress and reproductive medicine are still conflicting.
Methods
The national lockdown imposed in Italy in March‐May 2020 and the consequent assisted reproductive techniques (ART) activity blockage allowed to evaluate the conception ability of couples who suffered the postponement of ART cycles. In particular, we collected anamnestic, anthropometrical and demographic data of those women attending ART straddling the lockdown period attending to the Fertility Centre of Reggio Emilia.
Results
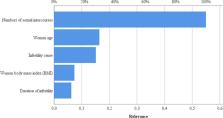
Among the 431 couples recalled to reschedule ART cycles, 34 couples (7.9%) obtained a spontaneous pregnancy during the lockdown. Comparing spontaneously pregnant to non‐pregnant women, the pregnant group resulted younger ( P = 0.009) and with a shorter infertility history ( P = 0.029). Interestingly, the sexual activity frequency was significantly higher in pregnant women compared to non‐pregnant ones ( P < 0.001). In a multivariate logistic analysis, number of sexual intercourses per week and the infertility history duration were significantly related to pregnancy ( P < 0.001 and P = 0.030, respectively). In addition, the application of neural network technology including data about women age, body mass index, infertility duration, weekly sexual intercourses and infertility causes allowed to correctly classify pregnant women with an accuracy of 92.7%.
Conclusion
The high pregnancy rate observed in a very short time‐frame interval probably revealed an under‐explored cause of idiopathic infertility, that is the frequency of sexual intercourses, resulting the best predictive variable on achieving a spontaneous pregnancy. This factor is commonly under‐investigated during the anamnestic workup of infertile couples. Clinicians involved in ART should better investigate the sexual habits of infertile couples, with the aim to correctly apply ART to those couples who really need it, avoiding unnecessary over‐treatment for those couples able to conceive spontaneously.
Related collections
Most cited references14
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A Novel Coronavirus from Patients with Pneumonia in China, 2019

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Immediate Psychological Responses and Associated Factors during the Initial Stage of the 2019 Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Epidemic among the General Population in China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
