- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Prevalence and antimicrobial resistance profiles of Salmonella spp. in poultry meat
Read this article at
Abstract
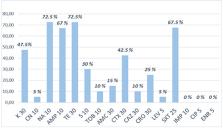
The spread of multidrug resistant (MDR) Salmonella strains, along the poultry supply chain, can represent a relevant threat to human health. This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence and antimicrobial resistance of Salmonella spp. isolated from poultry meat for human consumption. Between 2019 and 2021, 145 samples were analyzed according to ISO 6579-1:2017. The strains isolated were identified by using biochemical-enzymatic assays and serotyping, according to the Kauffmann-White-Le Minor scheme. The antibiotic susceptibility tests were determined using the Kirby-Bauer method. Forty Salmonella spp. strains were isolated and serotyping showed Salmonella Infantis to be predominant. 80% of the isolated strains were MDR and identified as S. Infantis. This study confirms the circulation of MDR Salmonella isolated from poultry meat and highlights the predominance of the S. Infantis serovar, which represents an emerging risk factor under the One Health holistic approach.
Related collections
Most cited references17
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Understanding the mechanisms and drivers of antimicrobial resistance.


- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found