- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The role of integrins in inflammation and angiogenesis
Read this article at
Abstract
Abstract
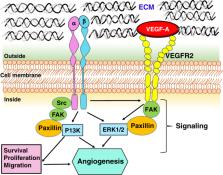
Integrins are heterodimeric transmembrane cell adhesion molecules made up of alpha (α) and beta (β) subunits arranged in numerous dimeric pairings. These complexes have varying affinities to extracellular ligands. Integrins regulate cellular growth, proliferation, migration, signaling, and cytokine activation and release and thereby play important roles in cell proliferation and migration, apoptosis, tissue repair, as well as in all processes critical to inflammation, infection, and angiogenesis. This review presents current evidence from human and animal studies on integrin structure and molecular signaling, with particular emphasis on signal transduction in infants. We have included evidence from our own laboratory studies and from an extensive literature search in databases PubMed, EMBASE, Scopus, and the electronic archives of abstracts presented at the annual meetings of the Pediatric Academic Societies. To avoid bias in identification of existing studies, key words were short-listed prior to the actual search both from anecdotal experience and from PubMed’s Medical Subject Heading (MeSH) thesaurus.
Impact
-
Integrins are a family of ubiquitous αβ heterodimeric receptors that interact with numerous ligands in physiology and disease. Integrins play a key role in cell proliferation, tissue repair, inflammation, infection, and angiogenesis.
-
This review summarizes current evidence from human and animal studies on integrin structure and molecular signaling and promising role in diseases of inflammation, infection, and angiogenesis in infants.
-
This review shows that integrin receptors and ligands are novel therapeutic targets of clinical interest and hold promise as novel therapeutic targets in the management of several neonatal diseases.
Related collections
Most cited references111
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Integrins in cancer: biological implications and therapeutic opportunities.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found