- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Leukemia Inhibitory Factor: Roles in Embryo Implantation and in Nonhormonal Contraception
review-article
Read this article at
There is no author summary for this article yet. Authors can add summaries to their articles on ScienceOpen to make them more accessible to a non-specialist audience.
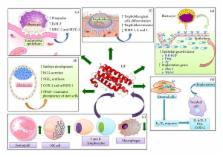
Abstract
Leukaemia inhibitory factor (LIF) plays an indispensible role in embryo implantation. Aberrant LIF production is linked to implantation failure. LIF regulates multiple processes prior to and during implantation such as uterine transformation into a receptive state, decidualization, blastocyst growth and development, embryo-endometrial interaction, trophoblast invasion, and immune modulation. Due to its critical role, LIF has been a target for a nonhormonal contraception. In this review, we summarize up-to-date information on the role of LIF in implantation and its role in contraception.
Related collections
Most cited references125
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The antiproliferative action of progesterone in uterine epithelium is mediated by Hand2.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Human pre-implantation embryo development.
K Niakan, Jinnuo Han, Carlos Simon … (2012)

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Th1:Th2 Dichotomy of Pregnancy and Preterm Labour
Lynne Sykes, David A. MacIntyre, Xiao Yap … (2012)