- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Dual Actions of Mammalian and Piscine Gonadotropin-Inhibitory Hormones, RFamide-Related Peptides and LPXRFamide Peptides, in the Hypothalamic–Pituitary–Gonadal Axis
Read this article at
Abstract
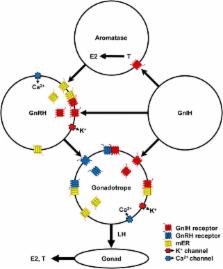
Gonadotropin-inhibitory hormone (GnIH) is a hypothalamic neuropeptide that decreases gonadotropin synthesis and release by directly acting on the gonadotrope or by decreasing the activity of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons. GnIH is also called RFamide-related peptide in mammals or LPXRFamide peptide in fishes due to its characteristic C-terminal structure. The primary receptor for GnIH is GPR147 that inhibits cAMP production in target cells. Although most of the studies in mammals, birds, and fish have shown the inhibitory action of GnIH in the hypothalamic–pituitary–gonadal (HPG) axis, several in vivo studies in mammals and many in vivo and in vitro studies in fish have shown its stimulatory action. In mouse, although the firing rate of the majority of GnRH neurons is decreased, a small population of GnRH neurons is stimulated by GnIH. In hamsters, GnIH inhibits luteinizing hormone (LH) release in the breeding season when their endogenous LH level is high but stimulates LH release in non-breeding season when their LH level is basal. Besides different effects of GnIH on the HPG axis depending on the reproductive stages in fish, higher concentration or longer duration of GnIH administration can stimulate their HPG axis. These results suggest that GnIH action in the HPG axis is modulated by sex-steroid concentration, the action of neuroestrogen synthesized by the activity of aromatase stimulated by GnIH, estrogen membrane receptor, heteromerization and internalization of GnIH, GnRH, and estrogen membrane receptors. The inhibitory and stimulatory action of GnIH in the HPG axis may have a physiological role to maintain reproductive homeostasis according to developmental and reproductive stages.
Related collections
Most cited references116
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Cloning of a novel receptor expressed in rat prostate and ovary.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Estrogen-induced activation of Erk-1 and Erk-2 requires the G protein-coupled receptor homolog, GPR30, and occurs via trans-activation of the epidermal growth factor receptor through release of HB-EGF.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found