- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
S1 ribosomal protein and the interplay between translation and mRNA decay
Read this article at
Abstract
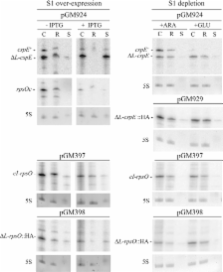
S1 is an ‘atypical’ ribosomal protein weakly associated with the 30S subunit that has been implicated in translation, transcription and control of RNA stability. S1 is thought to participate in translation initiation complex formation by assisting 30S positioning in the translation initiation region, but little is known about its role in other RNA transactions. In this work, we have analysed in vivo the effects of different intracellular S1 concentrations, from depletion to overexpression, on translation, decay and intracellular distribution of leadered and leaderless messenger RNAs (mRNAs). We show that the cspE mRNA, like the rpsO transcript, may be cleaved by RNase E at multiple sites, whereas the leaderless cspE transcript may also be degraded via an alternative pathway by an unknown endonuclease. Upon S1 overexpression, RNase E-dependent decay of both cspE and rpsO mRNAs is suppressed and these transcripts are stabilized, whereas cleavage of leaderless cspE mRNA by the unidentified endonuclease is not affected. Overall, our data suggest that ribosome-unbound S1 may inhibit translation and that part of the Escherichia coli ribosomes may actually lack S1.
Related collections
Most cited references63
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The critical role of RNA processing and degradation in the control of gene expression.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Lost in translation: the influence of ribosomes on bacterial mRNA decay.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found