- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Epidemiology of Respiratory Pathogens in Children with Severe Acute Respiratory Infection and Impact of the Multiplex PCR Film Array Respiratory Panel: A 2-Year Study
Read this article at
Abstract
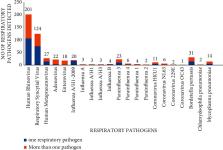
Sever acute respiratory infections (SARIs) are a public health issue that are common in children and are associated with an important morbidity and mortality rate worldwide. Although SARI are mainly caused by viruses, they are still a cause of antibiotic overuse. The use of molecular methods especially real-time multiplex PCR allowed to detect a wide range of respiratory viruses and their subtype as well as some atypical bacteria. The aim of this study was to investigate the epidemiology of respiratory pathogens detected in children admitted with SARI and to highlight the role of real-time multiplex PCR in the rapid diagnosis of viral and bacterial SARI. This work is a descriptive observational study from January 2018 to December 2019 including nasopharyngeal secretions collected from 534 children hospitalised in paediatric department. The detection of respiratory viruses and bacteria was performed by the FilmArray® Respiratory Panel. A total of 387 (72.5%) children were tested positive for at least one respiratory pathogen, and 23.3% of them were coinfected with more than one pathogen. Viral aetiology was found in 91.2% ( n = 340). The most common viruses detected were HRV ( n = 201) and RSV ( n = 124), followed by PIV ( n = 35) influenza A ( n = 29) and human metapneumovirus ( n = 27). Bacteria was found in 8.8% ( n = 47), and Bordetella pertussis was the most detected. Respiratory syncytial virus and Bordetella pertussis were significantly higher in infants less than 6 months old. The detection of RSV and influenza A presented a pic in winter, and HMPV was statistically significant in spring ( p < 0.01). This study described the epidemiology of respiratory pathogens involved in severe respiratory infections in children that were affected by several factors such as season and age group. It also highlighted the importance of multiplex PCR in confirming viral origin, thus avoiding irrational prescription of antibiotics in paediatric settings.
Related collections
Most cited references47
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Community-acquired pneumonia requiring hospitalization among U.S. children.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found