- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
ExDom: an integrated database for comparative analysis of the exon–intron structures of protein domains in eukaryotes
Read this article at
Abstract
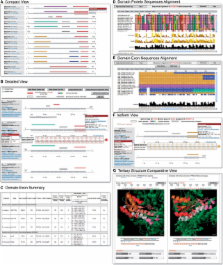
We have developed ExDom, a unique database for the comparative analysis of the exon–intron structures of 96 680 protein domains from seven eukaryotic organisms ( Homo sapiens, Mus musculus, Bos taurus, Rattus norvegicus, Danio rerio, Gallus gallus and Arabidopsis thaliana ). ExDom provides integrated access to exon-domain data through a sophisticated web interface which has the following analytical capabilities: (i) intergenomic and intragenomic comparative analysis of exon–intron structure of domains; (ii) color-coded graphical display of the domain architecture of proteins correlated with their corresponding exon-intron structures; (iii) graphical analysis of multiple sequence alignments of amino acid and coding nucleotide sequences of homologous protein domains from seven organisms; (iv) comparative graphical display of exon distributions within the tertiary structures of protein domains; and (v) visualization of exon–intron structures of alternative transcripts of a gene correlated to variations in the domain architecture of corresponding protein isoforms. These novel analytical features are highly suited for detailed investigations on the exon–intron structure of domains and make ExDom a powerful tool for exploring several key questions concerning the function, origin and evolution of genes and proteins. ExDom database is freely accessible at: http://66.170.16.154/ExDom/.
Related collections
Most cited references21
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Database resources of the National Center for Biotechnology Information

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found