- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effects of dulaglutide on endothelial progenitor cells and arterial elasticity in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Randomised controlled trial showed that dulaglutide can reduce the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease (ASCVD) in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), but the underlying mechanisms remain unclear. This study aimed to investigate the effect of dulaglutide on the number and function of endothelial progenitor cells (EPCs) in the peripheral blood of patients with T2DM and its role in improving arterial elasticity, so as to determine potential mechanisms of preventive effect of dulaglutide on ASCVD.
Methods
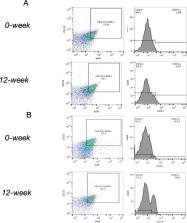
Sixty patients with T2DM were treated with 1000 mg/day of metformin and randomly divided into two groups for 12 weeks: metformin monotherapy group (MET group, n = 30), and metformin combined with dulaglutide group (MET-DUL group, n = 30). Before and after treatment, the number of CD34 +CD133 +KDR + EPCs and the brachial–ankle pulse wave velocity (baPWV) of the participants were measured, and EPC proliferation, adhesion, migration, and tubule formation were assessed in vitro.
Results
There were no significant differences in the number and function of EPCs and baPWV changes in MET group ( P > 0.05). In MET-DUL group, nitric oxide (NO) levels and the number of EPCs increased after treatment ( P < 0.05), while the levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), interleukin-6 (IL-6), tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF-α), advanced glycation end products (AGEs), and baPWV decreased ( P < 0.05). EPC proliferation, adhesion, migration, and tubule formation abilities were significantly enhanced ( P < 0.05). Correlation analysis showed that in MET-DUL group, the changes in CRP, IL-6, TNF-α, and AGEs were negatively correlated with the number of EPCs and their proliferation and migration abilities ( P < 0.05). Body weight, NO, CRP, and IL-6 levels were independent factors affecting the number of EPCs ( P < 0.05). The changes in number of EPCs, proliferation and migration abilities of EPCs, and NO and IL-6 levels were independent influencing factors of baPWV changes ( P < 0.05).
Conclusion
Dulaglutide can increase the number and function of EPCs in peripheral blood and improve arterial elasticity in patients with T2DM; it is accompanied by weight loss, inflammation reduction, and high NO levels. Dulaglutide regulation of EPCs may be a mechanism of cardiovascular protection.
Related collections
Most cited references56
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Dulaglutide and cardiovascular outcomes in type 2 diabetes (REWIND): a double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled trial
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Recent advances in the relationship between obesity, inflammation, and insulin resistance.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found