- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cervical cancer screening, treatment and prophylaxis in Brazil: Current and future perspectives for cervical cancer elimination
Read this article at
Abstract
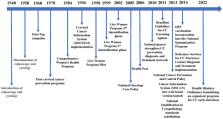
As a middle-income country, Brazil has one of the largest public health systems worldwide, which deals with free and universal access to health care. Regarding cervical cancer, the country possesses a large infrastructure for the screening of premalignant and malignant lesions, but yet based on old technology, having Papanicolaou as the major screening method, followed by colposcopy and treatment. Also, large disparities in access are present, which makes effectiveness of screening and treatment in different regions of the country highly unequal. In this review, we describe and evaluate the current screening, treatment and prophylactic (HPV vaccination) strategies to combat cervical cancer in Brazil, and discuss potential incorporation of more recent technologies in these areas in the country to pave its way toward cervical cancer elimination.
Related collections
Most cited references61
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Efficacy of HPV-based screening for prevention of invasive cervical cancer: follow-up of four European randomised controlled trials.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Evidence regarding human papillomavirus testing in secondary prevention of cervical cancer.
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.