- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Dual-Linear Kalman Filter for Real-Time Orientation Determination System Using Low-Cost MEMS Sensors
Read this article at
Abstract
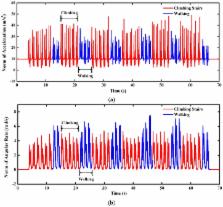
To provide a long-time reliable orientation, sensor fusion technologies are widely used to integrate available inertial sensors for the low-cost orientation estimation. In this paper, a novel dual-linear Kalman filter was designed for a multi-sensor system integrating MEMS gyros, an accelerometer, and a magnetometer. The proposed filter precludes the impacts of magnetic disturbances on the pitch and roll which the heading is subjected to. The filter can achieve robust orientation estimation for different statistical models of the sensors. The root mean square errors (RMSE) of the estimated attitude angles are reduced by 30.6% under magnetic disturbances. Owing to the reduction of system complexity achieved by smaller matrix operations, the mean total time consumption is reduced by 23.8%. Meanwhile, the separated filter offers greater flexibility for the system configuration, as it is possible to switch on or off the second stage filter to include or exclude the magnetometer compensation for the heading. Online experiments were performed on the homemade miniature orientation determination system (MODS) with the turntable. The average RMSE of estimated orientation are less than 0.4° and 1° during the static and low-dynamic tests, respectively. More realistic tests on two-wheel self-balancing vehicle driving and indoor pedestrian walking were carried out to evaluate the performance of the designed MODS when high accelerations and angular rates were introduced. Test results demonstrate that the MODS is applicable for the orientation estimation under various dynamic conditions. This paper provides a feasible alternative for low-cost orientation determination.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Pedestrian Tracking with shoe-mounted inertial sensors.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
