- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The mechanism of Shoutai Wan in the treatment of recurrent spontaneous abortion - A review

Read this article at
Abstract
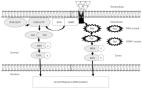
Recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA) is a prevalent pregnancy complication with a complex and poorly understood pathogenesis. Shoutai Wan (STW), a traditional Chinese medicine formula, is renowned for its kidney tonifying and fetus tranquilizing effects. It is used to treat miscarriages associated with kidney deficiency, hyperemesis gravidarum, and fetal restlessness. Recently, there has been an increase in experimental studies exploring the use of STW for RSA treatment, making progress in understanding its molecular mechanisms and signaling pathways. This review aims to systematically elucidate the mechanisms by which STW enhances cellular antioxidant capacity, attenuates inflammation, and improves the environment for embryo implantation. This involves regulating multiple signaling pathways, including Nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2/Heme oxygenase-1, JAK kinase 1/Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3, NOD-like receptor pyrin domain-containing protein/Caspase-1/Gasdermin D, Human Leukocyte Antigen G, Mitogen-activated protein kinase, and Serum and glucocorticoid-regulated kinase 1/Epithelial sodium channel. This review provides a theoretical reference for the clinical application and further experimental researches on the treatment of RSA with STW.
Related collections
Most cited references65
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Role of Nrf2/HO-1 system in development, oxidative stress response and diseases: an evolutionarily conserved mechanism
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found