- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Inter-observer agreement of the Coronary Artery Disease Reporting and Data System (CAD-RADS TM) in patients with stable chest pain
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose
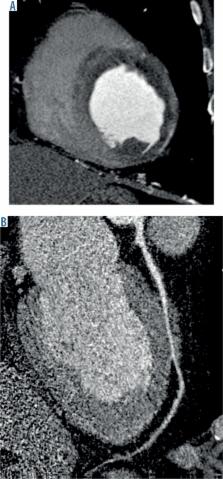
To assess inter-observer variability of the Coronary Artery Disease – Reporting and Data System (CAD-RADS) for classifying the degree of coronary artery stenosis in patients with stable chest pain.
Material and methods
A prospective study was conducted upon 96 patients with coronary artery disease, who underwent coronary computed tomography angiography (CTA). The images were classified using the CAD-RAD system according to the degree of stenosis, the presence of a modifier: graft (G), stent (S), vulnerable plaque (V), or non-diagnostic (n) and the associated coronary anomalies, and non-coronary cardiac and extra-cardiac findings. Image analysis was performed by two reviewers. Inter-observer agreement was assessed.
Results
There was excellent inter-observer agreement for CAD-RADS ( k = 0.862), at 88.5%. There was excellent agreement for CAD-RADS 0 ( k = 1.0), CAD-RADS 1 ( k = 0.92), CAD-RADS 3 ( k = 0.808), CAD-RADS 4 ( k = 0.826), and CAD-RADS 5 ( k = 0.833) and good agreement for CAD-RADS 2 ( k = 0.76). There was excellent agreement for modifier G ( k = 1.0) and modifier S ( k = 1.0), good agreement for modifier N ( k = 0.79), and moderate agreement for modifier V ( k = 0.59). There was excellent agreement for associated coronary artery anomalies ( k = 0.845), non-coronary cardiac findings ( k = 0.857), and extra-cardiac findings ( k = 0.81).
Related collections
Most cited references38
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
CAD-RADS(TM) Coronary Artery Disease - Reporting and Data System. An expert consensus document of the Society of Cardiovascular Computed Tomography (SCCT), the American College of Radiology (ACR) and the North American Society for Cardiovascular Imaging (NASCI). Endorsed by the American College of Cardiology.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Thyroid Ultrasound Reporting Lexicon: White Paper of the ACR Thyroid Imaging, Reporting and Data System (TIRADS) Committee.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found