- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Autophagy and cancer
Read this article at
Abstract
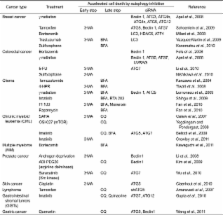
Basal autophagy plays a critical role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and genomic integrity by degrading aged or malfunctioning organelles and damaged or misfolded proteins. However, autophagy also plays a complicated role in tumorigenesis and treatment responsiveness. It can be tumor-suppressing during the early stages of tumorigenesis (i.e., it is an anti-tumor mechanism), as reduced autophagy is found in tumor cells and may be associated with malignant transformation. In this case, induction of autophagy would seem to be beneficial for cancer prevention. In established tumors, however, autophagy can be tumor-promoting (i.e., it is a pro-tumor mechanism), and cancer cells can use enhanced autophagy to survive under metabolic and therapeutic stress. The pharmacological and/or genetic inhibition of autophagy was recently shown to sensitize cancer cells to the lethal effects of various cancer therapies, including chemotherapy, radiotherapy and targeted therapies, suggesting that suppression of the autophagic pathway may represent a valuable sensitizing strategy for cancer treatments. In contrast, excessive stimulation of autophagy may also provide a therapeutic strategy for treating resistant cancer cells having high apoptotic thresholds. In order for us to develop successful autophagy-modulating strategies against cancer, we need to better understand how the roles of autophagy differ depending on the tumor stage, cell type and/or genetic factors, and we need to determine how specific pathways of autophagy are activated or inhibited by the various anti-cancer therapies.
Related collections
Most cited references87
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Beclin 1, an autophagy gene essential for early embryonic development, is a haploinsufficient tumor suppressor.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Life and death partners: apoptosis, autophagy and the cross-talk between them.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found