- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Variation of temperature increase rate in the Northern Hemisphere according to latitude, longitude and altitude: the Turkey example
Read this article at
Abstract
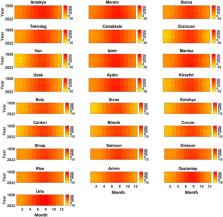
Global climate change notably influences meteorological variables such as temperature, affecting regions and countries worldwide. In this study, monthly average temperature data spanning 73 years (1950–2022) were analyzed for 28 stations in the city centers across seven regions of Turkey. The station warming rates (SWR) were calculated for selected stations and the overall country using Singular Spectrum Analysis (SSA) and Least Square Polynomial Fit (LSPF) methods. The temperature trend in Turkey exhibited a decline until the late 1970s, followed by a continuous rise due to global warming. Between 1980 and 2022, the average SWR in Turkey was found to be 0.52 °C/decade. The SWR was determined to be the lowest in Antakya (0.28 °C/decade) and the highest in Erzincan (0.69 °C/decade). The relationship between SWR and latitude, longitude, altitude, and distance to Null Island (D2NI) was explored through linear regression analysis. Altitude and D2NI were found to be the most significant variables, influencing the SWR. For altitude, the correlation coefficient (R) was 0.39 with a statistically significant value ( p) of 0.039. For D2NI, R, and p values were 0.39 and 0.038, respectively. Furthermore, in the multiple regression analysis involving altitude and D2NI, R and p values were determined to be 0.50 and 0.029, respectively. Furthermore, the collinearity analysis indicates no collinearity between altitude and D2NI, suggesting that their effects are separated in the multiple regression.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Decadal trends in the north atlantic oscillation: regional temperatures and precipitation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Increased aridity in the Mediterranean region under greenhouse gas forcing estimated from high resolution simulations with a regional climate model
Author and article information
Comments
Comment on this article
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.