- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sandwich osteotomy with interpositional grafts for vertical augmentation of the mandible: A meta-analysis
Read this article at
ABSTRACT
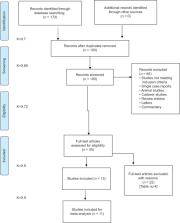
Sandwich osteotomy is a technique for vertical augmentation based on the principle of a graft being placed between two pedicled native bones. The inherent vascularization helps in graft consolidation. The aim is to review the bone height gained, implant survival and pitfalls with sandwich osteotomy. The PICO model was used to identify the suitable studies for the review. Oxford level of evidence, Newcastle Ottawa Scale and Cochrane's tool for Systematic Reviews of Interventions was applied for identifying study quality. Meta-analysis was performed with the help of RevMan. Funnel plot was used to evaluate publication bias and bias during article selection. Difference in means was used as principal summary measure. Fixed effects model with inverse variance statistics was used. I2test statistics was applied to identify study heterogeneity. Forest plots were produced for the outcome variables with 95% confidence interval (CI) and overall treatment effects and subgroup effects at a significance level of 0.05. The overall implant survival rate ranged from 90%-100% and prosthetic survival rate from 87%-95%. An overall 6-10mm of bone can be gained in the anterior mandible and 4-8mm in the posterior mandible. A total of 1030 implants were placed of which 988 implants survived after the mean follow up periods (odds ratio: 0.77, 95% CI: 0.49-1.21). Implant survival is independent of the graft being used. Vertical augmentation in the posterior mandible is limited compared to anterior owing to the presence of inferior alveolar nerve and the keratinized tissue deficiency.
Related collections
Most cited references28
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Synthesis without meta-analysis (SWiM) in systematic reviews: reporting guideline

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The impact of patient, intervention, comparison, outcome (PICO) as a search strategy tool on literature search quality: a systematic review
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found