- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
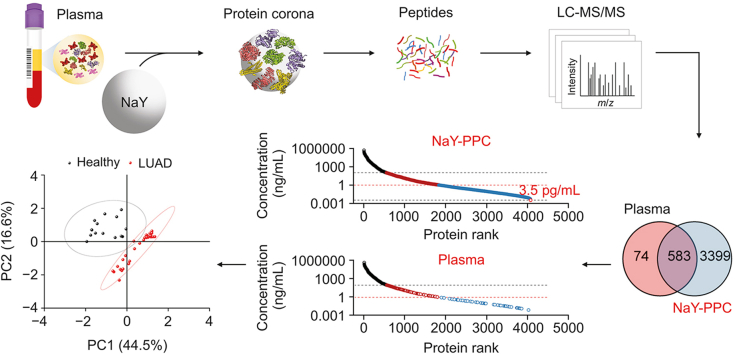
Comprehensive and deep profiling of the plasma proteome with protein corona on zeolite NaY

Read this article at
Abstract
Proteomic characterization of plasma is critical for the development of novel pharmacodynamic biomarkers. However, the vast dynamic range renders the profiling of proteomes extremely challenging. Here, we synthesized zeolite NaY and developed a simple and rapid method to achieve comprehensive and deep profiling of the plasma proteome using the plasma protein corona formed on zeolite NaY. Specifically, zeolite NaY and plasma were co-incubated to form plasma protein corona on zeolite NaY (NaY-PPC), followed by conventional protein identification using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. NaY was able to significantly enhance the detection of low-abundance plasma proteins, minimizing the “masking” effect caused by high-abundance proteins. The relative abundance of middle- and low-abundance proteins increased substantially from 2.54% to 54.41%, and the top 20 high-abundance proteins decreased from 83.63% to 25.77%. Notably, our method can quantify approximately 4000 plasma proteins with sensitivity up to pg/mL, compared to only about 600 proteins identified from untreated plasma samples. A pilot study based on plasma samples from 30 lung adenocarcinoma patients and 15 healthy subjects demonstrated that our method could successfully distinguish between healthy and disease states. In summary, this work provides an advantageous tool for the exploration of plasma proteomics and its translational applications.
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Plasma proteomics analysis based on protein corona on zeolite NaY was first proposed.
-
•
This method required only one type of particle, zeolite NaY.
-
•
NaY significantly enhanced the detection of low abundance plasma proteins.
-
•
Approximately 4000 proteins can be stably detected in a single-run LC-MS/MS.
-
•
A dynamic range of 8 orders of magnitude can be covered with sensitivity up to pg/mL.
Related collections
Most cited references7
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Human Plasma Proteome Draft of 2017: Building on the Human Plasma PeptideAtlas from Mass Spectrometry and Complementary Assays.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found