- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Curcumin inhibits spike protein of new SARS-CoV-2 variant of concern (VOC) Omicron, an in silico study

Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Omicron (B.1.1.529), a variant of SARS-CoV-2 is currently spreading globally as a dominant strain. Due to multiple mutations at its Spike protein, including 15 amino acid substitutions at the receptor binding domain (RBD), Omicron is a variant of concern (VOC) and capable of escaping vaccine generated immunity. So far, no specific treatment regime is suggested for this VOC.
Methods
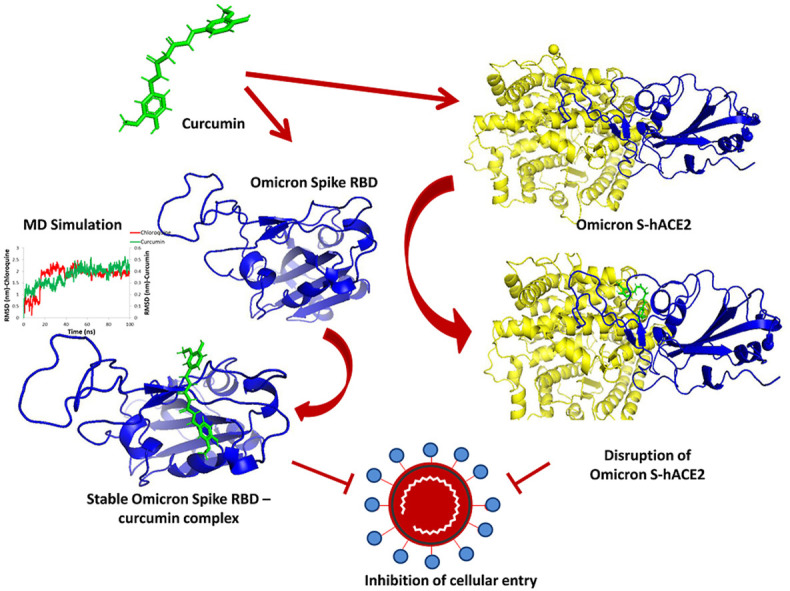
The three-dimensional structure of the Spike RBD domain of Omicron variant was constructed by incorporating 15 amino acid substitutions to the Native Spike (S) structure and structural changes were compared that of the Native S. Seven phytochemicals namely Allicin, Capsaicin, Cinnamaldehyde, Curcumin, Gingerol, Piperine, and Zingeberene were docked with Omicron S protein and Omicron S-hACE2 complex. Further, molecular dynamic simulation was performed between Crcumin and Omicron S protein to evaluate the structural stability of the complex in the physiological environment and compared with that of the control drug Chloroquine.
Results
Curcumin, among seven phytochemicals, was found to have the most substantial inhibitory potential with Omicron S protein. Further, it was found that curcumin could disrupt the Omicron S-hACE2 complex. The molecular dynamic simulation demonstrated that Curcumin could form a stable structure with Omicron S in the physiological environment.
Graphical abstract
Related collections
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Tracking changes in SARS-CoV-2 Spike: evidence that D614G increases infectivity of the COVID-19 virus
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
SARS-CoV-2 variants, spike mutations and immune escape
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found