- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
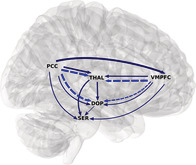
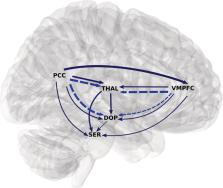
Interrelations between dopamine and serotonin producing sites and regions of the default mode network
Read this article at
Abstract
Recent functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) studies showed that blood oxygenation level‐dependent (BOLD) signal fluctuations in the default mode network (DMN) are functionally tightly connected to those in monoaminergic nuclei, producing dopamine (DA), and serotonin (5‐HT) transmitters, in the midbrain/brainstem. We combined accelerated fMRI acquisition with spectral Granger causality and coherence analysis to investigate causal relationships between these areas. Both methods independently lead to similar results and confirm the existence of a top‐down information flow in the resting‐state condition, where activity in core DMN areas influences activity in the neuromodulatory centers producing DA/5‐HT. We found that latencies range from milliseconds to seconds with high inter‐subject variability, likely attributable to the resting condition. Our novel findings provide new insights into the functional organization of the human brain.
Abstract
Related collections
Most cited references94
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Estimating the Dimension of a Model
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Investigating Causal Relations by Econometric Models and Cross-spectral Methods
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found