- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Anode Catalysts in CO 2 Electrolysis: Challenges and Untapped Opportunities

Read this article at
Abstract
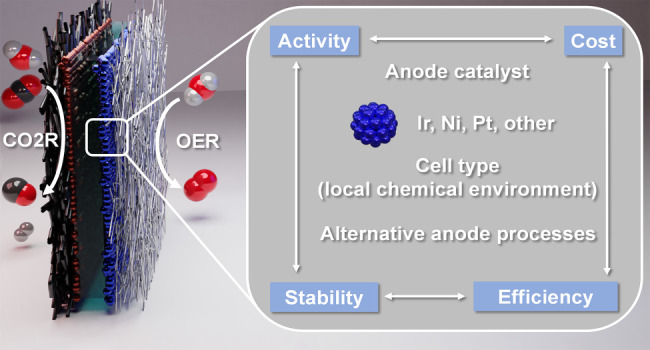
The field of electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction has developed rapidly during recent years. At the same time, the role of the anodic half-reaction has received considerably less attention. In this Perspective, we scrutinize the reports on the best-performing CO 2 electrolyzer cells from the past 5 years, to shed light on the role of the anodic oxygen evolution catalyst. We analyze how different cell architectures provide different local chemical environments at the anode surface, which in turn determines the pool of applicable anode catalysts. We uncover the factors that led to either a strikingly high current density operation or an exceptionally long lifetime. On the basis of our analysis, we provide a set of criteria that have to be fulfilled by an anode catalyst to achieve high performance. Finally, we provide an outlook on using alternative anode reactions (alcohol oxidation is discussed as an example), resulting in high-value products and higher energy efficiency for the overall process.
Related collections
Most cited references171
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Progress and Perspectives of Electrochemical CO2 Reduction on Copper in Aqueous Electrolyte
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
CO2electroreduction to ethylene via hydroxide-mediated copper catalysis at an abrupt interface
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found