- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Role of BRCA Mutations in Cancer Treatment with Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase (PARP) Inhibitors
Read this article at
Abstract
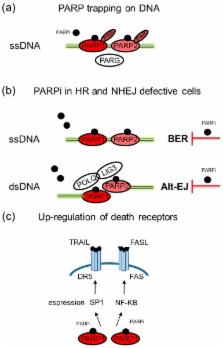
Inhibition of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) activity induces synthetic lethality in mutated BRCA1/2 cancers by selectively targeting tumor cells that fail to repair DNA double strand breaks (DSBs). Clinical studies have confirmed the validity of the synthetic lethality approach and four different PARP inhibitors (PARPi; olaparib, rucaparib, niraparib and talazoparib) have been approved as monotherapies for BRCA-mutated or platinum-sensitive recurrent ovarian cancer and/or for BRCA-mutated HER2-negative metastatic breast cancer. PARPi therapeutic efficacy is higher against tumors harboring deleterious germline or somatic BRCA mutations than in BRCA wild-type tumors. BRCA mutations or intrinsic tumor sensitivity to platinum compounds are both regarded as indicators of deficiency in DSB repair by homologous recombination as well as of favorable response to PARPi. However, not all BRCA-mutated or platinum-responsive patients obtain clinical benefit from these agents. Conversely, a certain percentage of patients with wild-type BRCA or platinum-resistant tumors can still get benefit from PARPi. Thus, additional reliable markers need to be validated in clinical trials to select patients potentially eligible for PARPi-based therapies, in the absence of deleterious BRCA mutations or platinum sensitivity. In this review, we summarize the mechanisms of action of PARPi and the clinical evidence supporting their use as anticancer drugs as well as the additional synthetic lethal partners that might confer sensitivity to PARPi in patients with wild-type BRCA tumors.
Related collections
Most cited references53
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
DNA double-strand breaks: signaling, repair and the cancer connection.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Oral poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor olaparib in patients with BRCA1 or BRCA2 mutations and recurrent ovarian cancer: a proof-of-concept trial.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found