- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effect of interventional embolotherapy on FHIT and p16 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma patients
Read this article at
Abstract
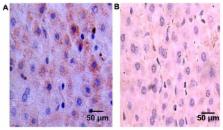
Effects of interventional embolotherapy on the expression of fragile histidine triad (FHIT) and p16 in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients were investigated. Patients with primary HCC who were definitely diagnosed and treated in the Department of Gastroenterology in Qingdao Central Hospital from March 2014 to March 2016 were selected, and they underwent interventional embolotherapy. HCC and cancer-adjacent tissues of the patients were harvested for immunohistochemical staining. The correlation between the expression levels of FHIT and p16 was analyzed at the gene and protein level. Clinical data were collected, and whether they were correlated with the expression of FHIT and p16 was investigated. The expression levels of FHIT and p16 in primary HCC tissues were remarkably lower than that in cancer-adjacent tissues (P<0.05). In HCC tissues, FHIT expression was obviously positively correlated with p16 expression (Spearman's correlation coefficient, r=0.308; P=0.025). FHIT was related to HCC tumor-node-metastasis (TNM) staging, the differentiation degree in Edmondson-Steiner grading, lymph node metastasis and portal vein thrombosis (P<0.05 in all comparisons), whereas, p16 was associated with tumor size and the differentiation degree in Edmondson-Steiner grading (P<0.05 in all comparisons). The expression of FHIT and p16 genes and proteins in HCC tissues were obviously lower than those in cancer-adjacent tissues (P<0.05 in all comparisons). FHIT and p16 genes, as tumor suppressor genes, inhibit the proliferation of HCC, and there is a positive correlation between them. The proteins of the FHIT and p16 can be used as new indicators for clinical detection, thus providing a new method for clinical diagnosis.
Related collections
Most cited references20
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Impact of HPV-associated p16-expression on radiotherapy outcome in advanced oropharynx and non-oropharynx cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Prognostic Relevance of HPV Infection and p16 Overexpression in Squamous Cell Anal Cancer.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found