- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Determinants of Health Seeking Behavior among Caregivers of Infants Admitted with Acute Childhood Illnesses at Kenyatta National Hospital, Nairobi, Kenya
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
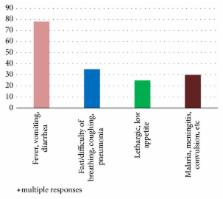
Poor, delayed, or inappropriate health seeking for a sick infant with acute childhood illness is associated with high morbidity/mortality. Delay in health seeking is implicated with fatal complications and prolonged hospital stay. Thus, caregivers ought to identify danger signs and promptly seek professional help for a sick infant.
Objective
Establish determinants of health seeking behavior among caregivers of infants admitted with acute childhood illnesses in Kenyatta National Hospital.
Methods
A mixed method cross-sectional study involving caregivers (n=130) of sick infants. Semistructured questionnaire and two focused group discussions were used to gather data on caregiver knowledge on danger signs, health care seeking options, and decision-making regarding health care seeking. Data was analyzed with SPSS V. 22.
Results
Knowledge of danger signs of infancy was poor. Immediate health seeking was associated with tertiary [P=0.009] and secondary [P=0.030] education, knowledgeability on danger signs [P=0.002], and being married [P=0.019]. Respondents who resided in urban [P=0.034] or less than a kilometer [P=0.042] from a health facility sought care immediately. Those who rated services as excellent (P=0.005) and satisfactory (P=0.025) sought care promptly.
Conclusion
Poor knowledge on danger signs of infancy was common among caregivers blurring the magnitude of acute illness resulting in delayed health seeking. Knowledgeability of danger signs of infancy, high educational level, and being married were associated with immediate health care seeking. Caregivers who resided in urban setting and/or near a health facility were linked to immediate health seeking. Additionally, satisfaction and perception of quality health care services were associated with immediate health seeking. Interventions with caregivers should involve capacity building through partnership with families and communities to raise awareness of danger signs of infancy. Strengthening of health care system to offer quality basic health services could improve health seeking behavior. Provision of a seamless supply system, infrastructural support, and technical support for soft skills minimize the turnaround time which is critical.
Related collections
Most cited references18
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Determinants of health care seeking for childhood illnesses in Nairobi slums.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Treatment-seeking behaviour, cost burdens and coping strategies among rural and urban households in Coastal Kenya: an equity analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found