- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Randomised clinical trial for morphological changes of trabecular meshwork between Kahook dual-blade goniotomy and ab interno trabeculotomy with a microhook
Read this article at
Abstract
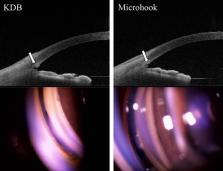
We demonstrated whether the difference of trabecular meshwork remodeling occur depending on the incisional cross-sectional area by comparing Kahook dual-blade goniotomy (KDB) and ab interno trabeculotomy with a microhook. Phakic eyes with primary open-angle or exfoliative glaucoma were randomised into a KDB or a microhook group. The primary outcome was an incisional cross-sectional area quantified by anterior segment optical coherence tomography. In subgroup analysis, the number of patients with the unidentifiable incisional area was compared between the groups. Secondary outcomes were the rate of intraocular pressure changes, the laser flare metre values, corneal endothelial cell densities, the number of glaucoma medications, the usage rate per glaucoma medication type and postoperative complications between the two groups. A total of 29 eyes in 29 patients in the KDB and microhook group were included respectively, with an overall mean age of 72.6 ± 8.1 years. The incisional cross-sectional area of the KDB group was significantly larger at 1 week and at 1, 6 and 12 months ( p < 0.01) postoperatively. The number of patients with the nonidentified incisional area was higher at 1, 6 and 12 months postoperatively ( p ≤ 0.03) in the microhook group. The flare values in the KDB group were higher than those in the microhook group at 12 months postoperatively ( p = 0.02). No significant differences were observed in other secondary outcomes. Incisional cross-sectional area remains larger in eyes treated with KDB goniotomy than in those treated with ab interno trabeculotomy with the microhook, whereas KDB goniotomy did not have an advantage in controlling intraocular pressure postoperatively.
Trial registration: UMIN000041290 (UMIN, University Hospital Medical Information Network Clinical Trials Registry of Japan; date of access and registration, 03/08/2020).
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The number of people with glaucoma worldwide in 2010 and 2020.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found