- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Advancing Preoperative Strategies for Thyroidectomy in Graves’ Disease: A Narrative Review
Read this article at
Abstract
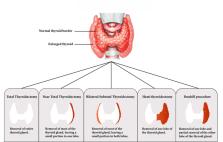
Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder characterized by thyroid-stimulating antibodies that can potentially lead to thyrotoxicosis, goiter, skin disease, and eye disease. Available treatment options for Graves' disease include management with antithyroid drugs (ATDs), thyroid ablation with radioactive iodine (RAI), and surgical thyroid gland removal. For individuals unable to reach a normal thyroid hormone level, promptly considering a thyroidectomy is essential. Preoperative strategies to achieve a euthyroid state prevent thyroid storms and minimize postoperative complications and are therefore crucial. While variations in professional guidance exist, this review focuses on standard medical interventions as well as compares respective guidelines set forth by the American Thyroid Association, the European Thyroid Association, the American Association of Clinical Endocrinology, and the American Association of Endocrine Surgeons. There is consensus among these organizations underscoring the importance of rendering patients euthyroid prior to surgery and the use of ATDs. Most guidelines recommend screening for vitamin D deficiency as well as endorse thyroidectomy as the preferred treatment option for hyperthyroidism with skilled surgeons. Nevertheless, discrepancies do become apparent in aspects such as potassium iodide (SSKI) course duration and preoperative dexamethasone administration. By understanding these differing approaches, healthcare professionals can more effectively manage Graves' disease prior to surgery, resulting in improved patient outcomes and enhanced surgical success.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
2016 American Thyroid Association Guidelines for Diagnosis and Management of Hyperthyroidism and Other Causes of Thyrotoxicosis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
2018 European Thyroid Association Guideline for the Management of Graves’ Hyperthyroidism
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found