- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Mosquito Behavior Change After Distribution of Bednets Results in Decreased Protection Against Malaria Exposure
Read this article at
Abstract
Background.
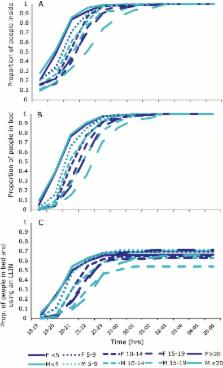
Behavioral resilience in mosquitoes poses a significant challenge to mosquito control. Although behavior changes in anopheline vectors have been reported over the last decade, there are no empirical data to suggest they compromise the efficacy of vector control in reducing malaria transmission.
Methods.
In this study, we quantified human exposure to both bites and infective bites of a major malaria vector in Papua New Guinea over the course of 4 years surrounding nationwide bednet distribution. We also quantified malaria infection prevalence in the human population during the same time period.
Results.
We observed a shift in mosquito biting to earlier hours of the evening, before individuals are indoors and protected by bednets, followed by a return to preintervention biting rates. As a result, net users and non–net users experienced higher levels of transmission than before the intervention. The personal protection provided by a bednet decreased over the study period and was lowest in the adult population, who may be an important reservoir for transmission. Malaria prevalence decreased in only 1 of 3 study villages after the distribution.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The effect of malaria control on Plasmodium falciparum in Africa between 2000 and 2015

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Increased proportions of outdoor feeding among residual malaria vector populations following increased use of insecticide-treated nets in rural Tanzania

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found