- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Integrative analysis of cancer multimodality data identifying COPS5 as a novel biomarker of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
Read this article at
Abstract
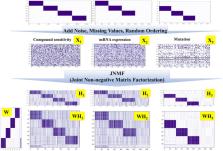
Preventing, diagnosing, and treating diseases requires accurate clinical biomarkers, which remains challenging. Recently, advanced computational approaches have accelerated the discovery of promising biomarkers from high-dimensional multimodal data. Although machine-learning methods have greatly contributed to the research fields, handling data sparseness, which is not unusual in research settings, is still an issue as it leads to limited interpretability and performance in the presence of missing information. Here, we propose a novel pipeline integrating joint non-negative matrix factorization (JNMF), identifying key features within sparse high-dimensional heterogeneous data, and a biological pathway analysis, interpreting the functionality of features by detecting activated signaling pathways. By applying our pipeline to large-scale public cancer datasets, we identified sets of genomic features relevant to specific cancer types as common pattern modules (CPMs) of JNMF. We further detected COPS5 as a potential upstream regulator of pathways associated with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL). COPS5 exhibited co-overexpression with MYC, TP53, and BCL2, known DLBCL marker genes, and its high expression was correlated with a lower survival probability of DLBCL patients. Using the CRISPR-Cas9 system, we confirmed the tumor growth effect of COPS5, which suggests it as a novel prognostic biomarker for DLBCL. Our results highlight that integrating multiple high-dimensional data and effectively decomposing them to interpretable dimensions unravels hidden biological importance, which enhances the discovery of clinical biomarkers.
Related collections
Most cited references30

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
GEPIA2: an enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Causal analysis approaches in Ingenuity Pathway Analysis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found