- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
B Cell Therapy in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: From Rationale to Clinical Practice
Read this article at
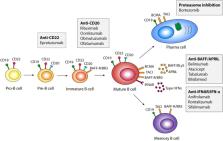
Abstract
B cell hyperactivity and breach of tolerance constitute hallmarks of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). The heterogeneity of disease manifestations and relatively rare prevalence of SLE have posed difficulties in trial design and contributed to a slow pace for drug development. The anti-BAFF monoclonal antibody belimumab is still the sole targeted therapy licensed for SLE, lending credence to the widely accepted notion that B cells play central roles in lupus pathogenesis. However, more therapeutic agents directed toward B cells or B cell-related pathways are used off-label or have been trialed in SLE. The anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab has been used to treat refractory SLE during the last two decades, and the anti-type I IFN receptor anifrolumab is currently awaiting approval after one phase III clinical trial which met its primary endpoint and one phase III trial which met key secondary endpoints. While the latter does not directly affect the maturation and antibody production activity of B cells, it is expected to affect the contribution of B cells in proinflammatory cytokine excretion. The proteasome inhibitor bortezomib, primarily directed toward the plasma cells, has been used in few severe cases as an escape regimen. Collectively, current clinical experience and primary results of ongoing clinical trials prophesy that B cell therapies of selective targets will have an established place in the future personalized therapeutic management of lupus patients.
Related collections
Most cited references83
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Combined oral contraceptives in women with systemic lupus erythematosus.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Lupus nephritis
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found