- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Immunosuppressive plasma cells impede T cell-dependent immunogenic chemotherapy
Read this article at
Abstract
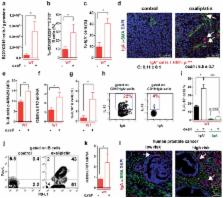
Cancer-associated genetic alterations induce expression of tumor antigens which can activate CD8 + cytotoxic T cells (CTL), but the microenvironment of established tumors promotes immune tolerance through poorly understood mechanisms 1, 2 . Recently developed therapeutics that overcome tolerogenic mechanisms activate tumor-directed CTL and are effective in some human cancers 1 . Immune mechanisms also affect treatment outcome and certain chemotherapeutic drugs stimulate cancer-specific immune responses by inducing immunogenic cell death (ICD) and other effector mechanisms 3, 4 . Our previous studies revealed that B lymphocytes recruited by CXCL13 into prostate cancer (PC) promote castrate-resistant PC (CRPC) by producing lymphotoxin (LT) which activates an IKKα-Bmi1 module in PC stem cells 5, 6 . Since CRPC is refractory to most therapies, we examined B cell involvement in acquisition of chemotherapy resistance. We focused this study on oxaliplatin, an immunogenic chemotherapeutic 3, 4 that is effective in aggressive PC 7 . We found that B cells modulate the response to low dose oxaliplatin, which by inducing ICD promotes tumor-directed CTL activation. Three different mouse PC models were refractory to oxaliplatin unless genetically or pharmacologically depleted of B cells. The critical immunosuppressive B cells are plasmocytes that express IgA, IL-10 and PD-L1, whose appearance depends on TGFβ-receptor (TGFβR) signaling. Elimination of these cells, which also infiltrate human therapy-resistant PC, allows CTL-dependent eradication of oxaliplatin-treated tumors.
Related collections
Most cited references38
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The blockade of immune checkpoints in cancer immunotherapy.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
T cell receptor antagonist peptides induce positive selection.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
