- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Application of Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System-Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II (ANFIS-NSGAII) for Modeling and Optimizing Somatic Embryogenesis of Chrysanthemum
Read this article at
Abstract
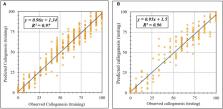
A hybrid artificial intelligence model and optimization algorithm could be a powerful approach for modeling and optimizing plant tissue culture procedures. The aim of this study was introducing an Adaptive Neuro-Fuzzy Inference System- Non-dominated Sorting Genetic Algorithm-II (ANFIS-NSGAII) as a powerful computational methodology for somatic embryogenesis of chrysanthemum, as a case study. ANFIS was used for modeling three outputs including callogenesis frequency (CF), embryogenesis frequency (EF), and the number of somatic embryo (NSE) based on different variables including 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), 6-benzylaminopurine (BAP), sucrose, glucose, fructose, and light quality. Subsequently, models were linked to NSGAII for optimizing the process, and the importance of each input was evaluated by sensitivity analysis. Results showed that all of the R 2 of training and testing sets were over 92%, indicating the efficiency and accuracy of ANFIS on the modeling of the embryogenesis. Also, according to ANFIS-NSGAII, optimal EF (99.1%), and NSE (13.1) can be obtained from a medium containing 1.53 mg/L 2,4-D, 1.67 mg/L BAP, 13.74 g/L sucrose, 57.20 g/L glucose, and 0.39 g/L fructose under red light. The results of the sensitivity analysis showed that embryogenesis was more sensitive to 2,4-D, and less sensitive to fructose. Generally, the hybrid ANFIS-NSGAII can be recognized as a powerful computational tool for modeling and optimizing in plant tissue culture.
Related collections
Most cited references61
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Plant Productivity in Response to LED Lighting
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cytokinin regulation of auxin synthesis in Arabidopsis involves a homeostatic feedback loop regulated via auxin and cytokinin signal transduction.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found