- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Can urban e-commerce transformation improve economic resilience? a quasi-natural experiment from China
Read this article at
Abstract
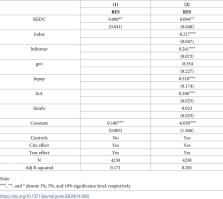
The impact of urban e-commerce transformation on economic resilience can help a country improve its ability to resist risks and seize the initiative in economic development. This study examines the impact of the construction of the National E-commerce Demonstration City (NEDC) on economic resilience using the staggered different-in-differences approach using a sample of 282 Chinese cities from 2006 to 2020. The results show NEDC construction significantly strengthens urban economic resilience. This result remains robust after undergoing placebo test, exclusion of other policies interference, and examining endogeneity. Furthermore, noteworthy heterogeneity exists in the effect of NEDC construction on urban economic resilience, particularly in eastern, developed regions, and cities with high Internet penetration. The mechanisms analysis indicates that NEDC construction enhances urban economic resilience by expanding the scale of urban employment and enhancing market dynamism. Overall, this study refines the causal relationship between e-commerce development and urban economic resilience, providing empirical evidence and policy insights for China and other countries to enhance urban economic resilience and stabilize macroeconomic fluctuations.
Related collections
Most cited references71
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Resilience and Stability of Ecological Systems
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
How Much Should We Trust Differences-In-Differences Estimates?
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found