- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Filling the gaps on stroke research: focus on inflammation and immunity

Read this article at
Highlights:
-
•
Efforts need to be done in preclinical research to select a clinically relevant experimental model of stroke, in terms of type of arterial occlusion and recanalization.
-
•
When testing immunomodulatory drugs, outcomes should include acute but also long-term measurements of both infarct volume and behavioral deficits.
-
•
Including coexisting risk factors in preclinical stroke research is mandatory.
Abstract
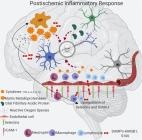
For the last two decades, researchers have placed hopes in a new era in which a combination of reperfusion and neuroprotection would revolutionize the treatment of stroke. Nevertheless, despite the thousands of papers available in the literature showing positive results in preclinical stroke models, randomized clinical trials have failed to show efficacy. It seems clear now that the existing data obtained in preclinical research have depicted an incomplete picture of stroke pathophysiology. In order to ameliorate bench-to-bed translation, in this review we first describe the main actors on stroke inflammatory and immune responses based on the available preclinical data, highlighting the fact that the link between leukocyte infiltration, lesion volume and neurological outcome remains unclear. We then describe what is known on neuroinflammation and immune responses in stroke patients, and summarize the results of the clinical trials on immunomodulatory drugs. In order to understand the gap between clinical trials and preclinical results on stroke, we discuss in detail the experimental results that served as the basis for the summarized clinical trials on immunomodulatory drugs, focusing on (i) experimental stroke models, (ii) the timing and selection of outcome measuring, (iii) alternative entry routes for leukocytes into the ischemic region, and (iv) factors affecting stroke outcome such as gender differences, ageing, comorbidities like hypertension and diabetes, obesity, tobacco, alcohol consumption and previous infections like Covid-19.
We can do better for stroke treatment, especially when targeting inflammation following stroke. We need to re-think the design of stroke experimental setups, notably by (i) using clinically relevant models of stroke, (ii) including both radiological and neurological outcomes, (iii) performing long-term follow-up studies, (iv) conducting large-scale preclinical stroke trials, and (v) including stroke comorbidities in preclinical research.
Related collections
Most cited references157
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Venous and arterial thromboembolic complications in COVID-19 patients admitted to an academic hospital in Milan, Italy
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Large-Vessel Stroke as a Presenting Feature of Covid-19 in the Young
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
