- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cystatin C deficiency suppresses tumor growth in a breast cancer model through decreased proliferation of tumor cells
Read this article at
Abstract
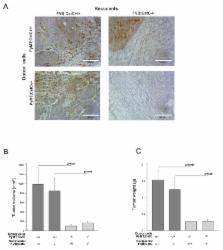
Cysteine cathepsins are proteases that, in addition to their important physiological functions, have been associated with multiple pathologies, including cancer. Cystatin C (CstC) is a major endogenous inhibitor that regulates the extracellular activity of cysteine cathepsins. We investigated the role of cystatin C in mammary cancer using CstC knockout mice and a mouse model of breast cancer induced by expression of the polyoma middle T oncoprotein (PyMT) in the mammary epithelium. We showed that the ablation of CstC reduced the rate of mammary tumor growth. Notably, a decrease in the proliferation of CstC knockout PyMT tumor cells was demonstrated ex vivo and in vitro, indicating a role for this protease inhibitor in signaling pathways that control cell proliferation. An increase in phosphorylated p-38 was observed in CstC knockout tumors, suggesting a novel function for cystatin C in cancer development, independent of the TGF-β pathway. Moreover, proteomic analysis of the CstC wild-type and knockout PyMT primary cell secretomes revealed a decrease in the levels of 14-3-3 proteins in the secretome of knock-out cells, suggesting a novel link between cysteine cathepsins, cystatin C and 14-3-3 proteins in tumorigenesis, calling for further investigations.
Related collections
Most cited references69
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Immunological hallmarks of stromal cells in the tumour microenvironment.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Comparison of label-free methods for quantifying human proteins by shotgun proteomics.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found