- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The lay descriptors of out-of-hospital cardiac arrest in the Western Cape province, South Africa
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest (OHCA) is a time-sensitive emergency requiring prompt identification and emergency care to reduce morbidity and mortality. The first step in managing OHCA is rapid identification by the emergency dispatch centre. Identification of these patients remains challenging in South Africa due to multiple languages and widely differing levels of education. This study aimed to identify the key descriptors (words and phrases) of OHCA used by callers in the Western Cape when contacting the provincial Emergency Medical Services' emergency call centre.
Methodology
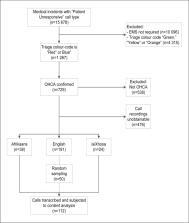
Computer-aided dispatch data with a corresponding “ patient unresponsive” incident type were drawn for a 12-month period (January–December 2018). Corresponding patient care records were extracted to verify OHCA. The original voice recordings between the caller and emergency call taker at the time of the emergency were extracted and transcribed verbatim. Transcriptions were subjected to inductive, qualitative content analysis to the manifest level. Descriptors of OHCA in isiXhosa, English and Afrikaans calls were coded, categorised, and quantified.
Results
A total of 729 confirmed OHCA cases were identified, of which 38 (5.2%) Afrikaans, 24 (3.3%) isiXhosa and a random sample of 50 (6.8%) English calls were transcribed. Following content analysis, five distinct categories were identified. The most prevalent categories were descriptors related to ill health (medical history and suspected diagnosis; 35.5%), level of consciousness (unresponsive; 18.6%) and cardiac activity (pulselessness and suspected death; 17.2%).
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Consolidated criteria for reporting qualitative research (COREQ): a 32-item checklist for interviews and focus groups.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Three approaches to qualitative content analysis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found