- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Iron deficiency induces female infertile in order to failure of follicular development in mice
Read this article at
Abstract
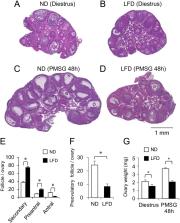
Iron is important for many cellular functions, including ATP synthesis and cell proliferation. Insufficient of iron in the diet causes iron deficiency anemia (IDA), which often occurs in people living in the world. Since 50% of women with IDA show amenorrhea, the relationship of between iron deficiency and reproductive function was assessed using mice fed a low Fe diet (LFD). The estrous cycle in the LFD mice was blocked at diestrus, which impair follicle development, and fertility. Further, even LFD mice were injected with exogenous pregnant mare serum gonadotropin (PMSG), follicular development was ceased at the secondary follicle stage, and preovulatory follicles were not observed. Amount of ATP decreased in the ovary of the LFD mice, and expression of follicle development markers ( Fshr, Cyp19a1, Ccnd2) and estradiol-17β (E2) was low level compared to levels mice fed a normal diet. Feeding a normal diet with sufficient iron to the LFD mice for an additional 3 weeks completely reversed absence the effects of iron insufficient on the estrous cycle and infertility. Thus, iron restriction depresses ovary functions, especially follicular development from secondary follicle to antral follicles and infertility. These effects are fully reversible by supplementation of a normal diet containing iron.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A systematic analysis of global anemia burden from 1990 to 2010.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Mouse Estrous Cycle Identification Tool and Images
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found