- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Frameless versus frame-based stereotactic radiosurgery for intracranial arteriovenous malformations: A propensity-matched analysis
Read this article at
Highlights
Abstract
Objective
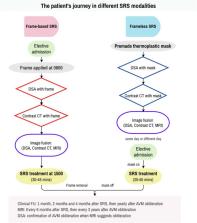
The frameless linear accelerator (LINAC) based stereotactic radiosurgery (SRS) has been evolving with a reduction in patient discomfort. However, there was limited evidence comparing frame-based and frameless SRS for intracranial arteriovenous malformations (AVM). We aimed to compare the treatment outcomes between frame-based and frameless LINAC SRS.
Materials and Methods
This retrospective cohort compared the outcomes of frame-based LINAC SRS (1998–2009) with frameless LINAC SRS (2010–2020). The primary outcome was the obliteration rate. The other outcomes included the neurological, radiological, and functional outcomes after SRS. A matched cohort was identified by propensity scores for further comparisons.
Results
A total of 65 patients were included with a mean follow-up time of 13.2 years (158.5 months). There were 40 patients in the frame-based group and 25 patients in the frameless group. The overall obliteration rate was comparable (Frame-based 82.5% vs Frameless 80.0%, p = 0.310) and not significantly different over time (log-rank p = 0.536). The crude post-SRS hemorrhage rate was 1.5% and the incidence was 0.3 per 100 person-years. There were 67.7% of patients with AVM obliteration without new persistent neurological deficits at the last visit and 56.9% of patients with AVM obliteration without any deficits (transient or persistent) during the entire follow-up period. Four patients (8.0%) developed late onset persistent adverse radiation effects (more than 96 months after SRS) among 50 patients with more than 8-year surveillance. In the propensity-matched cohort of 42 patients, there was no significant difference in AVM obliteration (Frame-based vs Frameless, log-rank p = 0.984).
Related collections
Most cited references39
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A proposed grading system for arteriovenous malformations.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Some methods of propensity-score matching had superior performance to others: results of an empirical investigation and Monte Carlo simulations.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found