- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Interplay between mitochondrial reactive oxygen species, oxidative stress and hypoxic adaptation in facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy: Metabolic stress as potential therapeutic target
Read this article at
Abstract
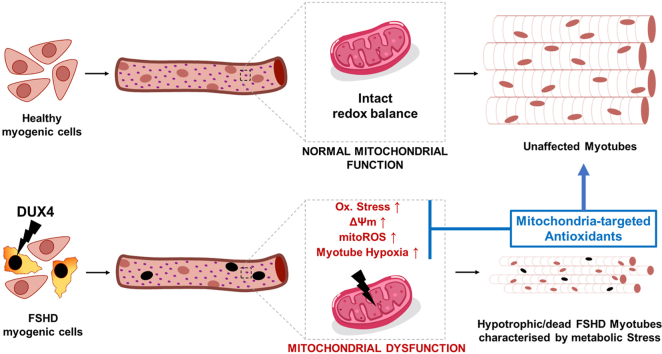
Facioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSHD) is characterised by descending skeletal muscle weakness and wasting. FSHD is caused by mis-expression of the transcription factor DUX4, which is linked to oxidative stress, a condition especially detrimental to skeletal muscle with its high metabolic activity and energy demands. Oxidative damage characterises FSHD and recent work suggests metabolic dysfunction and perturbed hypoxia signalling as novel pathomechanisms. However, redox biology of FSHD remains poorly understood, and integrating the complex dynamics of DUX4-induced metabolic changes is lacking.
Here we pinpoint the kinetic involvement of altered mitochondrial ROS metabolism and impaired mitochondrial function in aetiology of oxidative stress in FSHD. Transcriptomic analysis in FSHD muscle biopsies reveals strong enrichment for pathways involved in mitochondrial complex I assembly, nitrogen metabolism, oxidative stress response and hypoxia signalling. We found elevated mitochondrial ROS (mitoROS) levels correlate with increases in steady-state mitochondrial membrane potential in FSHD myogenic cells. DUX4 triggers mitochondrial membrane polarisation prior to oxidative stress generation and apoptosis through mitoROS, and affects mitochondrial health through lipid peroxidation. We identify complex I as the primary target for DUX4-induced mitochondrial dysfunction, with strong correlation between complex I-linked respiration and cellular oxygenation/hypoxia signalling activity in environmental hypoxia. Thus, FSHD myogenesis is uniquely susceptible to hypoxia-induced oxidative stress as a consequence of metabolic mis-adaptation. Importantly, mitochondria-targeted antioxidants rescue FSHD pathology more effectively than conventional antioxidants, highlighting the central involvement of disturbed mitochondrial ROS metabolism. This work provides a pathomechanistic model by which DUX4-induced changes in oxidative metabolism impair muscle function in FSHD, amplified when metabolic adaptation to varying O 2 tension is required.
Graphical abstract
Highlights
-
•
Transcriptomics data from FSHD muscle indicates enrichment for disturbed mitochondrial pathways.
-
•
Disturbed mitochondrial ROS metabolism correlates with mitochondrial membrane polarisation and myotube hypotrophy.
-
•
DUX4-induced changes in mitochondrial function precede mitoROS generation and affect hypoxia signalling via complex I.
-
•
FSHD is sensitive to environmental hypoxia, which increases ROS levels in FSHD myotubes.
-
•
Hypotrophy in hypoxic FSHD myotubes is efficiently rescued with mitochondria-targeted antioxidants.
Related collections
Most cited references127
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
edgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found