- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A phase 3 study of safety and immunogenicity of V114, a 15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine, followed by 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine, in children with HIV

Read this article at
Objectives:
To evaluate the safety and immunogenicity of V114 [15-valent pneumococcal conjugate vaccine (PCV) containing serotypes 1, 3, 4, 5, 6A, 6B, 7F, 9 V, 14, 18C, 19A, 19F, 22F, 23F, 33F], followed by 23-valent pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccine (PPSV23) 8 weeks later, in children with HIV.
Design:
This phase 3 study (NCT03921424) randomized participants 6–17 years of age with HIV (CD4 + T-cell count ≥200 cells/μl, plasma HIV RNA <50 000 copies/ml) to receive V114 or 13-valent PCV (PCV13) in a double-blind manner on Day 1, followed by PPSV23 at Week 8.
Methods:
Adverse events (AEs), pneumococcal serotype-specific immunoglobulin G (IgG), and opsonophagocytic activity (OPA) were evaluated 30 days after each vaccination.
Results:
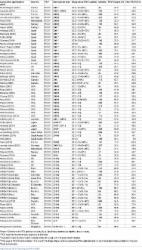
The proportion of participants experiencing at least one AE post-PCV was 78.8% in the V114 group ( n = 203) and 69.6% in the PCV13 group ( n = 204); respective proportions post-PPSV23 were 75.4% ( n = 203) and 77.2% ( n = 202). There were no vaccine-related serious AEs. IgG geometric mean concentrations (GMCs) and OPA geometric mean titers (GMTs) were generally comparable between V114 and PCV13 for shared serotypes at Day 30, and were higher for V114 compared with PCV13 for the additional V114 serotypes 22F and 33F. Approximately 30 days after PPSV23, IgG GMCs and OPA GMTs were generally comparable between the V114 and PCV13 groups for all 15 serotypes in V114.
Related collections
Most cited references25
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The Use of Confidence or Fiducial Limits Illustrated in the Case of the Binomial
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found