- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Strain vs. charge mediated magnetoelectric coupling across the magnetic oxide/ferroelectric interfaces

Read this article at
Abstract
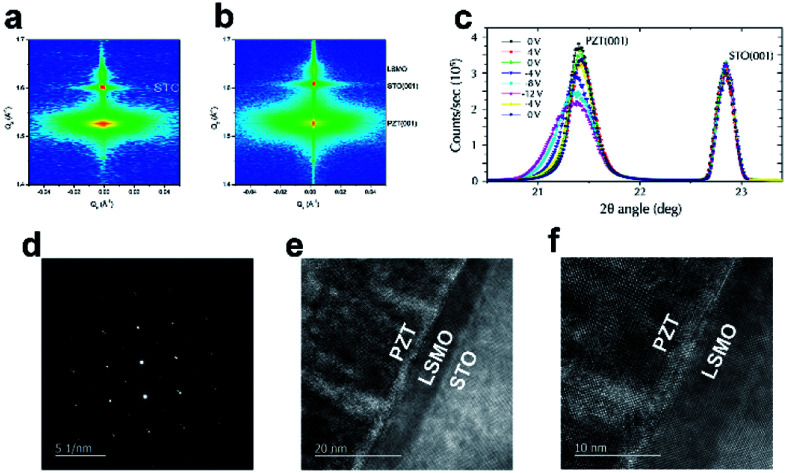
We utilize polarized neutron reflectometry (PNR) in consort with ab initio based density functional theory (DFT) calculations to study magnetoelectric coupling at the interface of a ferroelectric PbZr 0.2Ti 0.8O 3 (PZT) and magnetic La 0.67Sr 0.33MnO 3 (LSMO) heterostructure grown on a Nb-doped SrTiO 3 (001) substrate. Functional device working conditions are mimicked by gating the heterostructure with a Pt top electrode to apply an external electric field, which alters the magnitude and switches the direction of the ferroelectric (FE) polarization, across the PZT layer. PNR results show that the gated PZT/LSMO exhibits interfacial magnetic phase modulation attributed to ferromagnetic (FM) to A-antiferromagnetic (A-AF) phase transitions resulting from hole accumulation. When the net FE polarization points towards the interface (positive), the interface doesn't undergo a magnetic phase transition and retains its global FM ordered state. In addition to changes in the interfacial magnetic ordering, the global magnetization of LSMO increases while switching the polarization from positive to negative and decreases vice versa. DFT calculations indicate that this enhanced magnetization also correlates with an out of plane tensile strain, whereas the suppressed magnetization for positive polarization is attributed to out of plane compressive strain. These calculations also show the coexistence of FM and A-AF phases at zero out of plane strain. Charge modulations throughout the LSMO layer appear to be unaffected by strain, suggesting that these charge mediated effects do not significantly change the global magnetization. Our PNR results and DFT calculations are in consort to verify that the interfacial magnetic modulations are due to co-action of strain and charge mediated effects with the strain and charge effects dominant at different length scale.
Abstract
We utilize polarized neutron reflectometry in consort with ab initio based density functional theory calculations to study interface magnetoelectric coupling across a ferroelectric PbZr 0.2Ti 0.8O 3 and magnetic La 0.67Sr 0.33MnO 3 heterostructure.
Related collections
Most cited references4
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
QUANTUM ESPRESSO: a modular and open-source software project for quantum simulations of materials.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Book: not found
Neutron Scattering from Magnetic Materials
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Book: not found