- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Entrepreneurial mental health in the wake of COVID-19 in China with an emphasis on attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and dyslexia analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
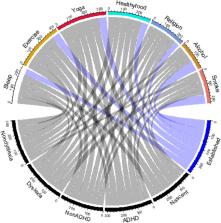
The COVID-19 pandemic has precipitated a global mental health crisis, with a particularly pronounced impact on the entrepreneurial sector. This paper presents a comparative analysis of mental health challenges among entrepreneurs in China during the pandemic, with a specific focus on attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and Dyslexia. The study assesses the prevalence of ADHD and dyslexia symptoms among established and emerging entrepreneurs in China, finding notable occurrences within this group. The research also examines the self-care practices of these entrepreneurs, shedding light on their approaches during the pandemic period. The findings highlight a complex interplay between mental health issues and entrepreneurial activities, suggesting that certain ADHD and dyslexia traits may offer unexpected benefits in the entrepreneurial realm. These insights are critical for developing supportive frameworks that leverage the strengths of neurodiverse entrepreneurs while mitigating associated challenges, especially in a post-pandemic economic landscape. The study concludes with policy and practice recommendations to bolster the wellbeing and resilience of entrepreneurs facing the multifaceted impacts of the pandemic.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The Satisfaction With Life Scale.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The prevalence and correlates of adult ADHD in the United States: results from the National Comorbidity Survey Replication.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found