- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
ABA-Mediated Stomatal Response in Regulating Water Use during the Development of Terminal Drought in Wheat
Read this article at
Abstract
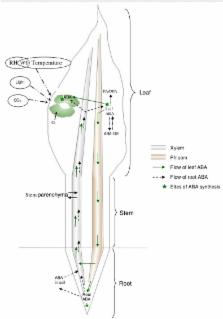
End-of-season drought or “terminal drought,” which occurs after flowering, is considered the most significant abiotic stress affecting crop yields. Wheat crop production in Mediterranean-type environments is often exposed to terminal drought due to decreasing rainfall and rapid increases in temperature and evapotranspiration during spring when wheat crops enter the reproductive stage. Under such conditions, every millimeter of extra soil water extracted by the roots benefits grain filling and yield and improves water use efficiency (WUE). When terminal drought develops, soil dries from the top, exposing the top part of the root system to dry soil while the bottom part is in contact with available soil water. Plant roots sense the drying soil and produce signals, which on transmission to shoots trigger stomatal closure to regulate crop water use through transpiration. However, transpiration is linked to crop growth and productivity and limiting transpiration may reduce potential yield. While an early and high degree of stomatal closure affects photosynthesis and hence biomass production, a late and low degree of stomatal closure exhausts available soil water rapidly which results in yield losses through a reduction in post-anthesis water use. The plant hormone abscisic acid (ABA) is considered the major chemical signal involved in stomatal regulation. Wheat genotypes differ in their ability to produce ABA under drought and also in their stomatal sensitivity to ABA. In this viewpoint article we discuss the possibilities of exploiting genotypic differences in ABA response to soil drying in regulating the use of water under terminal drought. Root density distribution in the upper drying layers of the soil profile is identified as a candidate trait that can affect ABA accumulation and subsequent stomatal closure. We also examine whether leaf ABA can be designated as a surrogate characteristic for improved WUE in wheat to sustain grain yield under terminal drought. Ease of collecting leaf samples to quantify ABA compared to extracting xylem sap will facilitate rapid screening of a large number of germplasm for drought tolerance.
Related collections
Most cited references144
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Photosynthetic carbon assimilation and associated metabolism in relation to water deficits in higher plants.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Abscisic Acid and Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Crop Plants
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found